|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| media | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
This is a guide to using YubiKey as a SmartCard for storing GPG encryption, signing and authentication keys, which can also be used for SSH. Many of the principles in this document are applicable to other smart card devices.
Keys stored on YubiKey are non-exportable (as opposed to file-based keys that are stored on disk) and are convenient for everyday use. Instead of having to remember and enter passphrases to unlock SSH/GPG keys, YubiKey needs only a physical touch after being unlocked with a PIN code. All signing and encryption operations happen on the card, rather than in OS memory.
New! drduh/Purse is a password manager which uses GPG and YubiKey.
If you have a comment or suggestion, please open an Issue on GitHub.
- Purchase YubiKey
- Verify YubiKey
- Download OS image
- Required software
- Creating keys
- Master key
- Sub-keys
- Verify
- Export
- Backup
- Configure Smartcard
- Transfer keys
- Verify card
- Cleanup
- Using keys
- Rotating keys
- SSH
- Multiple Keys
- Require touch
- Reset
- Notes
- Troubleshooting
- Links
Purchase YubiKey
All YubiKeys except the blue "security key" model are compatible with this guide. NEO models are limited to 2048-bit RSA keys. Compare YubiKeys here.
Verify YubiKey
To verify a YubiKey is genuine, open a browser with U2F support to https://www.yubico.com/genuine/. Insert a Yubico device, and select Verify Device to begin the process. Touch the YubiKey when prompted, and if asked, allow it to see the make and model of the device. If you see Verification complete, the device is authentic.
This website verifies the YubiKey's device attestation certificates signed by a set of Yubico CAs, and helps mitigate supply chain attacks.
Download OS Image
You will need several small storage devices for booting a temporary operating system and creating backups of your private/public keys.
It is recommended to generate cryptographic keys and configure YubiKey from a secure operating system and using an ephemeral environment ("live image"), such as Debian, Tails, or OpenBSD booted from a USB drive.
Depending on your threat model and/or level of inherent trust in your own system. It is also a valid option to run the "live image" within a VM using something like Virtualbox or VMWare
To use Debian, download the latest image:
$ curl -LfO https://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/current-live/amd64/iso-hybrid/debian-live-10.0.0-amd64-xfce.iso
$ curl -LfO https://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/current-live/amd64/iso-hybrid/SHA512SUMS
$ curl -LfO https://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/current-live/amd64/iso-hybrid/SHA512SUMS.sign
Verify file integrity with GPG:
$ gpg --verify SHA512SUMS.sign SHA512SUMS
gpg: Signature made Sat Jul 6 18:51:32 2019 PDT
gpg: using RSA key DF9B9C49EAA9298432589D76DA87E80D6294BE9B
gpg: Can't check signature: No public key
$ gpg --recv DF9B9C49EAA9298432589D76DA87E80D6294BE9B
gpg: key 0xDA87E80D6294BE9B: 61 signatures not checked due to missing keys
gpg: key 0xDA87E80D6294BE9B: public key "Debian CD signing key <debian-cd@lists.debian.org>" imported
gpg: marginals needed: 3 completes needed: 1 trust model: pgp
gpg: depth: 0 valid: 1 signed: 0 trust: 0-, 0q, 0n, 0m, 0f, 1u
gpg: Total number processed: 1
gpg: imported: 1
$ gpg --verify SHA512SUMS.sign SHA512SUMS
gpg: Signature made Sat Jul 6 18:51:32 2019 PDT
gpg: using RSA key DF9B9C49EAA9298432589D76DA87E80D6294BE9B
gpg: Good signature from "Debian CD signing key <debian-cd@lists.debian.org>" [unknown]
gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature!
gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner.
Primary key fingerprint: DF9B 9C49 EAA9 2984 3258 9D76 DA87 E80D 6294 BE9B
$ grep $(sha512sum debian-live-10.0.0-amd64-xfce.iso) SHA512SUMS
SHA512SUMS:c230dc15705bbae07782185af7f933ed7821ec94fa4b9d08a61856b27cdf7d3a4e9f5b6ddb419b96714464ca76c2686083fc4534dc116cc9980b52c233331e03 debian-live-10.0.0-amd64-xfce.iso
If the key cannot be received, try changing the DNS resolver and/or use a specific keyserver:
$ gpg --keyserver hkps://keyserver.ubuntu.com:443 --recv DF9B9C49EAA9298432589D76DA87E80D6294BE9B
See Verifying authenticity of Debian CDs for more information.
Mount a storage device and copy the image to it:
Linux
$ sudo dmesg | tail
usb-storage 3-2:1.0: USB Mass Storage device detected
scsi host2: usb-storage 3-2:1.0
scsi 2:0:0:0: Direct-Access TS-RDF5 SD Transcend TS3A PQ: 0 ANSI: 6
sd 2:0:0:0: Attached scsi generic sg1 type 0
sd 2:0:0:0: [sdb] 31116288 512-byte logical blocks: (15.9 GB/14.8 GiB)
sd 2:0:0:0: [sdb] Write Protect is off
sd 2:0:0:0: [sdb] Mode Sense: 23 00 00 00
sd 2:0:0:0: [sdb] Write cache: disabled, read cache: enabled, doesn't support DPO or FUA
sdb: sdb1 sdb2
sd 2:0:0:0: [sdb] Attached SCSI removable disk
$ sudo dd if=debian-live-10.0.0-amd64-xfce.iso of=/dev/sdb bs=4M
465+1 records in
465+1 records out
1951432704 bytes (2.0 GB, 1.8 GiB) copied, 42.8543 s, 45.5 MB/s
OpenBSD
$ dmesg | tail -n2
sd2 at scsibus4 targ 1 lun 0: <TS-RDF5, SD Transcend, TS3A> SCSI4 0/direct removable serial.0000000000000
sd2: 15193MB, 512 bytes/sector, 31116288 sectors
$ doas dd if=debian-live-10.0.0-amd64-xfce.iso of=/dev/rsd2c bs=4m
465+1 records in
465+1 records out
1951432704 bytes transferred in 139.125 secs (14026448 bytes/sec)
Shut down the computer and disconnect internal hard drives and all unnecessary peripheral devices. If being run within a VM this part can be skipped as no such devices should be attached to the VM since the image will still be run as a "live image"
If on physical hardware consider using secure hardware like a ThinkPad X230 running Coreboot and cleaned of Intel ME.
Required software
Boot the OS image and configure networking.
Note If the screen locks, unlock with user/live.
Open the terminal and install required software packages.
Debian/Ubuntu
Note Live Ubuntu images may require modification to /etc/apt/sources.list
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y \
gnupg2 gnupg-agent dirmngr \
cryptsetup scdaemon pcscd \
secure-delete hopenpgp-tools \
yubikey-personalization
Arch
$ sudo pacman -Syu \
gnupg2 pcsclite ccid hopenpgp-tools \
yubikey-personalization
RHEL7
$ sudo yum install -y \
gnupg2 pinentry-curses pcsc-lite pcsc-lite-libs gnupg2-smime
OpenBSD
$ doas pkg_add gnupg pcsc-tools
macOS
Download and install Homebrew and the following Brew packages:
$ brew install gnupg yubikey-personalization hopenpgp-tools ykman pinentry-mac
Windows
Download and install Gpg4Win and PuTTY.
You may also need more recent versions of yubikey-personalization and yubico-c.
Entropy
Generating cryptographic keys requires high-quality randomness, measured as entropy.
To check the available entropy available on Linux:
$ cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/entropy_avail
849
Most operating systems use software-based pseudorandom number generators. A hardware random number generator like OneRNG will increase the speed of entropy generation and possibly the quality.
Install and configure OneRNG software:
$ sudo apt install -y \
at rng-tools python-gnupg openssl
$ wget https://github.com/OneRNG/onerng.github.io/raw/master/sw/onerng_3.6-1_all.deb
$ sha256sum onerng_3.6-1_all.deb
a9ccf7b04ee317dbfc91518542301e2d60ebe205d38e80563f29aac7cd845ccb onerng_3.6-1_all.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i onerng_3.6-1_all.deb
$ echo "HRNGDEVICE=/dev/ttyACM0" | sudo tee /etc/default/rng-tools
Plug in the device and restart rng-tools:
$ sudo atd
$ sudo service rng-tools restart
Test by emptying /dev/random - the light on the device will dim briefly:
$ cat /dev/random >/dev/null
[Press Control-C]
After a few seconds, verify the available entropy pool is quickly re-seeded:
$ cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/entropy_avail
3049
An entropy pool value greater than 2000 is sufficient.
Creating keys
Create a temporary directory which will be cleared on reboot:
$ export GNUPGHOME=$(mktemp -d)
$ cd $GNUPGHOME
Create a hardened configuration in the temporary directory with the following options:
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/drduh/config/master/gpg.conf
$ grep -ve "^#" $GNUPGHOME/gpg.conf
personal-cipher-preferences AES256 AES192 AES
personal-digest-preferences SHA512 SHA384 SHA256
personal-compress-preferences ZLIB BZIP2 ZIP Uncompressed
default-preference-list SHA512 SHA384 SHA256 AES256 AES192 AES ZLIB BZIP2 ZIP Uncompressed
cert-digest-algo SHA512
s2k-digest-algo SHA512
s2k-cipher-algo AES256
charset utf-8
fixed-list-mode
no-comments
no-emit-version
keyid-format 0xlong
list-options show-uid-validity
verify-options show-uid-validity
with-fingerprint
require-cross-certification
no-symkey-cache
throw-keyids
use-agent
Disable networking for the remainder of the setup.
Master key
The first key to generate is the master key. It will be used for certification only: to issue sub-keys that are used for encryption, signing and authentication.
Important The master key should be kept offline at all times and only accessed to revoke or issue new sub-keys. Keys can also be generated on the YubiKey itself to ensure no other copies exist.
You'll be prompted to enter and verify a passphrase - keep it handy as you'll need it multiple times later.
To generate a strong passphrase which could be written down in a hidden or secure place; or memorized:
$ gpg --gen-random -a 0 24
ydOmByxmDe63u7gqx2XI9eDgpvJwibNH
On Linux or OpenBSD, select the password with the mouse to copy it to the clipboard and paste using the middle mouse button or Shift-Insert.
Generate a new key with GPG, selecting (8) RSA (set your own capabilities), Certify capability only and 4096 bit key size.
Do not set the master key to expire - see Note #3.
$ gpg --expert --full-generate-key
Please select what kind of key you want:
(1) RSA and RSA (default)
(2) DSA and Elgamal
(3) DSA (sign only)
(4) RSA (sign only)
(7) DSA (set your own capabilities)
(8) RSA (set your own capabilities)
(9) ECC and ECC
(10) ECC (sign only)
(11) ECC (set your own capabilities)
(13) Existing key
Your selection? 8
Possible actions for a RSA key: Sign Certify Encrypt Authenticate
Current allowed actions: Sign Certify Encrypt
(S) Toggle the sign capability
(E) Toggle the encrypt capability
(A) Toggle the authenticate capability
(Q) Finished
Your selection? E
Possible actions for a RSA key: Sign Certify Encrypt Authenticate
Current allowed actions: Sign Certify
(S) Toggle the sign capability
(E) Toggle the encrypt capability
(A) Toggle the authenticate capability
(Q) Finished
Your selection? S
Possible actions for a RSA key: Sign Certify Encrypt Authenticate
Current allowed actions: Certify
(S) Toggle the sign capability
(E) Toggle the encrypt capability
(A) Toggle the authenticate capability
(Q) Finished
Your selection? Q
RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
What keysize do you want? (2048) 4096
Requested keysize is 4096 bits
Please specify how long the key should be valid.
0 = key does not expire
<n> = key expires in n days
<n>w = key expires in n weeks
<n>m = key expires in n months
<n>y = key expires in n years
Key is valid for? (0) 0
Key does not expire at all
Is this correct? (y/N) y
Select a name and email address - neither has to be valid nor existing.
GnuPG needs to construct a user ID to identify your key.
Real name: Dr Duh
Email address: doc@duh.to
Comment: [Optional - leave blank]
You selected this USER-ID:
"Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>"
Change (N)ame, (C)omment, (E)mail or (O)kay/(Q)uit? o
We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
gpg: /tmp.FLZC0xcM/trustdb.gpg: trustdb created
gpg: key 0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB marked as ultimately trusted
gpg: directory '/tmp.FLZC0xcM/openpgp-revocs.d' created
gpg: revocation certificate stored as '/tmp.FLZC0xcM/openpgp-revocs.d/011CE16BD45B27A55BA8776DFF3E7D88647EBCDB.rev'
public and secret key created and signed.
pub rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB 2017-10-09 [C]
Key fingerprint = 011C E16B D45B 27A5 5BA8 776D FF3E 7D88 647E BCDB
uid Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
Export the key ID as a variable (KEYID) for use later:
$ export KEYID=0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
Sign with an existing key (optional)
If you already have a pgp key you may want to sign your new key with the old one to help prove that your new key is infact controlled by you.
Export your existing key to move it to the working keyring. From a different terminal do:
$ gpg --export-secret-keys --armor --output /tmp/new.sec
to export your old key and then
$ gpg --default-key $OLDKEY --sign-key $KEYID
Sub-keys
Edit the master key to add sub-keys:
$ gpg --expert --edit-key $KEYID
Secret key is available.
sec rsa4096/0xEA5DE91459B80592
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: C
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
Use 4096-bit key sizes.
Use a 1 year expiration for sub-keys - they can be renewed using the offline master key. See rotating keys.
Signing
Create a signing key by selecting (4) RSA (sign only):
gpg> addkey
Key is protected.
You need a passphrase to unlock the secret key for
user: "Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>"
4096-bit RSA key, ID 0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB, created 2016-05-24
Please select what kind of key you want:
(3) DSA (sign only)
(4) RSA (sign only)
(5) Elgamal (encrypt only)
(6) RSA (encrypt only)
(7) DSA (set your own capabilities)
(8) RSA (set your own capabilities)
Your selection? 4
RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
What keysize do you want? (2048) 4096
Requested keysize is 4096 bits
Please specify how long the key should be valid.
0 = key does not expire
<n> = key expires in n days
<n>w = key expires in n weeks
<n>m = key expires in n months
<n>y = key expires in n years
Key is valid for? (0) 1y
Key expires at Mon 10 Sep 2018 00:00:00 PM UTC
Is this correct? (y/N) y
Really create? (y/N) y
We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: C
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: S
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
Encryption
Next, create an encryption key by selecting (6) RSA (encrypt only):
gpg> addkey
Please select what kind of key you want:
(3) DSA (sign only)
(4) RSA (sign only)
(5) Elgamal (encrypt only)
(6) RSA (encrypt only)
(7) DSA (set your own capabilities)
(8) RSA (set your own capabilities)
(10) ECC (sign only)
(11) ECC (set your own capabilities)
(12) ECC (encrypt only)
(13) Existing key
Your selection? 6
RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
What keysize do you want? (2048) 4096
Requested keysize is 4096 bits
Please specify how long the key should be valid.
0 = key does not expire
<n> = key expires in n days
<n>w = key expires in n weeks
<n>m = key expires in n months
<n>y = key expires in n years
Key is valid for? (0) 1y
Key expires at Mon 10 Sep 2018 00:00:00 PM UTC
Is this correct? (y/N) y
Really create? (y/N) y
We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: C
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: S
ssb rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: E
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
Authentication
Finally, create an authentication key.
GPG doesn't provide an authenticate-only key type, so select (8) RSA (set your own capabilities) and toggle the required capabilities until the only allowed action is Authenticate:
gpg> addkey
Please select what kind of key you want:
(3) DSA (sign only)
(4) RSA (sign only)
(5) Elgamal (encrypt only)
(6) RSA (encrypt only)
(7) DSA (set your own capabilities)
(8) RSA (set your own capabilities)
(10) ECC (sign only)
(11) ECC (set your own capabilities)
(12) ECC (encrypt only)
(13) Existing key
Your selection? 8
Possible actions for a RSA key: Sign Encrypt Authenticate
Current allowed actions: Sign Encrypt
(S) Toggle the sign capability
(E) Toggle the encrypt capability
(A) Toggle the authenticate capability
(Q) Finished
Your selection? S
Possible actions for a RSA key: Sign Encrypt Authenticate
Current allowed actions: Encrypt
(S) Toggle the sign capability
(E) Toggle the encrypt capability
(A) Toggle the authenticate capability
(Q) Finished
Your selection? E
Possible actions for a RSA key: Sign Encrypt Authenticate
Current allowed actions:
(S) Toggle the sign capability
(E) Toggle the encrypt capability
(A) Toggle the authenticate capability
(Q) Finished
Your selection? A
Possible actions for a RSA key: Sign Encrypt Authenticate
Current allowed actions: Authenticate
(S) Toggle the sign capability
(E) Toggle the encrypt capability
(A) Toggle the authenticate capability
(Q) Finished
Your selection? Q
RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
What keysize do you want? (2048) 4096
Requested keysize is 4096 bits
Please specify how long the key should be valid.
0 = key does not expire
<n> = key expires in n days
<n>w = key expires in n weeks
<n>m = key expires in n months
<n>y = key expires in n years
Key is valid for? (0) 1y
Key expires at Mon 10 Sep 2018 00:00:00 PM UTC
Is this correct? (y/N) y
Really create? (y/N) y
We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: C
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: S
ssb rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: E
ssb rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: A
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
Finish by saving the keys.
gpg> save
Add extra emails
gpg> adduid
Real name: Dr Duh
Email address: DrDuh@other.org
Comment:
You selected this USER-ID:
"Dr Duh <DrDuh@other.org>"
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: SC
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: S
ssb rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: E
ssb rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: A
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
[ unknown] (2). Dr Duh <DrDuh@other.org>
gpg> trust
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: SC
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: S
ssb rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: E
ssb rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: A
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
[ unknown] (2). Dr Duh <DrDuh@other.org>
Please decide how far you trust this user to correctly verify other users' keys
(by looking at passports, checking fingerprints from different sources, etc.)
1 = I don't know or won't say
2 = I do NOT trust
3 = I trust marginally
4 = I trust fully
5 = I trust ultimately
m = back to the main menu
Your decision? 5
Do you really want to set this key to ultimate trust? (y/N) y
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: SC
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: S
ssb rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: E
ssb rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: A
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
[ unknown] (2). Dr Duh <DrDuh@other.org>
gpg> save
Verify
List the generated secret keys and verify the output:
$ gpg -K
/tmp.FLZC0xcM/pubring.kbx
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB 2017-10-09 [C]
Key fingerprint = 011C E16B D45B 27A5 5BA8 776D FF3E 7D88 647E BCDB
uid Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15 2017-10-09 [S] [expires: 2018-10-09]
ssb rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF 2017-10-09 [E] [expires: 2018-10-09]
ssb rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D 2017-10-09 [A] [expires: 2018-10-09]
Add any additional identities or email addresses you wish to associate using the adduid command.
Tip Verify with a OpenPGP key best practice checker:
$ gpg --export $KEYID | hokey lint
The output will display any problems with your key in red text. If everything is green, your key passes each of the tests. If it is red, your key has failed one of the tests.
hokey may warn (orange text) about cross certification for the authentication key. GPG's Signing Subkey Cross-Certification documentation has more detail on cross certification, and gpg v2.2.1 notes "subkey does not sign and so does not need to be cross-certified". hokey may also indicate a problem (red text) with
Key expiration times: []on the primary key (see Note #3 about not setting an expiry for the primary key).
Export
The master key and sub-keys will be encrypted with your passphrase when exported.
Save a copy of your keys:
$ gpg --armor --export-secret-keys $KEYID > $GNUPGHOME/mastersub.key
$ gpg --armor --export-secret-subkeys $KEYID > $GNUPGHOME/sub.key
On Windows, note that using any extension other than .gpg or attempting IO redirection to a file will garble the secret key, making it impossible to import it again at a later date:
$ gpg -o \path\to\dir\mastersub.gpg --armor --export-secret-keys $KEYID
$ gpg -o \path\to\dir\sub.gpg --armor --export-secret-subkeys $KEYID
Backup
Once GPG keys are moved to YubiKey, they cannot be moved again! Create an encrypted backup of the keyring and consider using a paper copy of the keys as an additional backup.
Tip: The ext2 filesystem (without encryption) can be mounted on both Linux and OpenBSD.
Linux
Attach another external storage device and check its label:
$ sudo dmesg | tail
usb-storage 4-2:1.0: USB Mass Storage device detected
scsi host7: usb-storage 4-2:1.0
scsi 7:0:0:0: Direct-Access TS-RDF5 SD Transcend TS37 PQ: 0 ANSI: 6
sd 7:0:0:0: Attached scsi generic sg1 type 0
sd 7:0:0:0: [sdb] 31116288 512-byte logical blocks: (15.9 GB/14.8 GiB)
sd 7:0:0:0: [sdb] Write Protect is off
sd 7:0:0:0: [sdb] Mode Sense: 23 00 00 00
sd 7:0:0:0: [sdb] Write cache: disabled, read cache: enabled, doesn't support DPO or FUA
sdb: sdb1
sd 7:0:0:0: [sdb] Attached SCSI removable disk
Write it with random data to prepare for encryption:
$ sudo dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/sdb bs=4M status=progress
Erase and create a new partition table:
$ sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.29.2).
Command (m for help): o
Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xeac7ee35.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
Create a new partition with a 10 Megabyte size:
$ sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.29.2).
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p):
Partition number (1-4, default 1):
First sector (2048-62980095, default 2048):
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-62980095, default 62980095): +10M
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 10 MiB.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
Use LUKS to encrypt the new partition:
$ sudo cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/sdb1
WARNING!
========
This will overwrite data on /dev/sdb1 irrevocably.
Are you sure? (Type uppercase yes): YES
Enter passphrase:
Verify passphrase:
Mount the partition:
$ sudo cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sdb1 usb
Enter passphrase for /dev/sdb1:
Create a filesystem:
$ sudo mkfs.ext2 /dev/mapper/usb -L usb
Creating filesystem with 10240 1k blocks and 2560 inodes
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
8193
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
Mount the filesystem and copy the temporary directory with the keyring:
$ sudo mkdir /mnt/encrypted-usb
$ sudo mount /dev/mapper/usb /mnt/encrypted-usb
$ sudo cp -avi $GNUPGHOME /mnt/encrypted-usb
Optional Backup the OneRNG package:
$ sudo cp onerng_3.6-1_all.deb /mnt/encrypted-usb
Keep the backup mounted if you plan on setting up two or more keys as keytocard will delete the local copy on save.
Otherwise, unmount and disconnected the encrypted volume:
$ sudo umount /mnt/encrypted-usb
$ sudo cryptsetup luksClose usb
Create another partition to store the public key, or skip this step if you plan on uploading it to a key server.
Important Without the public key, you will not be able to use GPG to encrypt, decrypt, nor sign messages. However, you will still be able to use YubiKey for SSH authentication.
$ sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p):
Partition number (2-4, default 2):
First sector (22528-31116287, default 22528):
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (22528-31116287, default 31116287): +10M
Created a new partition 2 of type 'Linux' and of size 10 MiB.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
$ sudo mkfs.ext2 /dev/sdb2
Creating filesystem with 10240 1k blocks and 2560 inodes
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
8193
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
$ sudo mkdir /mnt/public
$ sudo mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt/public/
$ gpg --armor --export $KEYID | sudo tee /mnt/public/$KEYID-$(date +%F).txt
Windows:
$ gpg -o \path\to\dir\pubkey.gpg --armor --export $KEYID
Optional Upload the public key to a public keyserver:
$ gpg --send-key $KEYID
$ gpg --keyserver pgp.mit.edu --send-key $KEYID
$ gpg --keyserver keys.gnupg.net --send-key $KEYID
$ gpg --keyserver hkps://keyserver.ubuntu.com:443 --send-key $KEYID
After some time, the public key will to propagate to other servers.
OpenBSD
Attach a USB disk and determine its label:
$ dmesg | grep sd.\ at
sd2 at scsibus5 targ 1 lun 0: <TS-RDF5, SD Transcend, TS37> SCSI4 0/direct removable serial.00000000000000000000
Print the existing partitions to make sure it's the right device:
$ doas disklabel -h sd2
Initialize the disk by creating an a partition with FS type RAID and size of 10 Megabytes:
$ doas fdisk -iy sd2
Writing MBR at offset 0.
$ doas disklabel -E sd2
Label editor (enter '?' for help at any prompt)
sd2> a a
offset: [64]
size: [31101776] 10M
FS type: [4.2BSD] RAID
sd2*> w
sd2> q
No label changes
Encrypt with bioctl:
$ doas bioctl -c C -l sd2a softraid0
New passphrase:
Re-type passphrase:
softraid0: CRYPTO volume attached as sd3
Create an i partition on the new crypto volume and the filesystem:
$ doas fdisk -iy sd3
Writing MBR at offset 0.
$ doas disklabel -E sd3
Label editor (enter '?' for help at any prompt)
sd3> a i
offset: [64]
size: [16001]
FS type: [4.2BSD]
sd3*> w
sd3> q
No label changes.
$ doas newfs sd3i
/dev/rsd3i: 7.8MB in 16000 sectors of 512 bytes
4 cylinder groups of 1.95MB, 125 blocks, 256 inodes each
super-block backups (for fsck -b #) at:
32, 4032, 8032, 12032,
Mount the filesystem and copy the temporary directory with the keyring:
$ doas mkdir /mnt/encrypted-usb
$ doas mount /dev/sd3i /mnt/encrypted-usb
$ doas cp -avi $GNUPGHOME /mnt/encrypted-usb
Keep the backup mounted if you plan on setting up two or more keys as keytocard will delete the local copy on save.
Otherwise, unmount and disconnected the encrypted volume:
$ doas umount /mnt/encrypted-usb
$ doas bioctl -d sd3
See OpenBSD FAQ#14 for more information.
Create another partition to store the public key, or skip this step if you plan on uploading it to a key server.
Important Without the public key, you will not be able to use GPG to encrypt, decrypt, nor sign messages. However, you will still be able to use YubiKey for SSH authentication.
$ doas disklabel -E sd2
Label editor (enter '?' for help at any prompt)
sd2> a b
offset: [32130]
size: [31069710] 10M
FS type: [swap] 4.2BSD
sd2*> w
sd2> q
No label changes.
$ doas newfs sd2b
/dev/rsd2b: 15.7MB in 32096 sectors of 512 bytes
5 cylinder groups of 3.89MB, 249 blocks, 512 inodes each
super-block backups (for fsck -b #) at:
32, 8000, 15968, 23936, 31904,
$ doas mkdir /mnt/public
$ doas mount /dev/sd2b /mnt/public
$ gpg --armor --export $KEYID | doas tee /mnt/public/$KEYID.txt
Configure Smartcard
Windows Use the YubiKey Manager application (note, this not the similarly named older YubiKey NEO Manager) to enable CCID functionality.
Use GPG to configure YubiKey as a smartcard:
$ gpg --card-edit
Reader ...........: Yubico Yubikey 4 OTP U2F CCID
Application ID ...: D2760001240102010006055532110000
Version ..........: 2.1
Manufacturer .....: Yubico
Serial number ....: 05553211
Name of cardholder: [not set]
Language prefs ...: [not set]
Sex ..............: unspecified
URL of public key : [not set]
Login data .......: [not set]
Signature PIN ....: not forced
Key attributes ...: rsa2048 rsa2048 rsa2048
Max. PIN lengths .: 127 127 127
PIN retry counter : 3 0 3
Signature counter : 0
Signature key ....: [none]
Encryption key....: [none]
Authentication key: [none]
General key info..: [none]
Change PIN
The default PIN is 123456 and default Admin PIN (PUK) is 12345678. CCID-mode PINs can be up to 127 ASCII characters.
The Admin PIN is required for some card operations and to unblock a PIN that has been entered incorrectly more than three times. See the GnuPG documentation on Managing PINs for details.
gpg/card> admin
Admin commands are allowed
gpg/card> passwd
gpg: OpenPGP card no. D2760001240102010006055532110000 detected
1 - change PIN
2 - unblock PIN
3 - change Admin PIN
4 - set the Reset Code
Q - quit
Your selection? 3
PIN changed.
1 - change PIN
2 - unblock PIN
3 - change Admin PIN
4 - set the Reset Code
Q - quit
Your selection? 1
PIN changed.
1 - change PIN
2 - unblock PIN
3 - change Admin PIN
4 - set the Reset Code
Q - quit
Your selection? q
Set information
Some fields are optional.
gpg/card> name
Cardholder's surname: Duh
Cardholder's given name: Dr
gpg/card> lang
Language preferences: en
gpg/card> login
Login data (account name): doc@duh.to
gpg/card> list
Application ID ...: D2760001240102010006055532110000
Version ..........: 2.1
Manufacturer .....: unknown
Serial number ....: 05553211
Name of cardholder: Dr Duh
Language prefs ...: en
Sex ..............: unspecified
URL of public key : [not set]
Login data .......: doc@duh.to
Private DO 4 .....: [not set]
Signature PIN ....: not forced
Key attributes ...: 2048R 2048R 2048R
Max. PIN lengths .: 127 127 127
PIN retry counter : 3 0 3
Signature counter : 0
Signature key ....: [none]
Encryption key....: [none]
Authentication key: [none]
General key info..: [none]
gpg/card> quit
Transfer keys
Important Transferring keys to YubiKey using keytocard is a destructive, one-way operation only. Make sure you've made a backup before proceeding: keytocard converts the local, on-disk key into a stub, which means the on-disk copy is no longer usable to transfer to subsequent security key devices or mint additional keys.
Previous GPG versions required the toggle command before selecting keys. The currently selected key(s) are indicated with an *. When moving keys only one key should be selected at a time.
$ gpg --edit-key $KEYID
Secret key is available.
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: C
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: S
ssb rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: E
ssb rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: A
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
Signing
Select and move the signature key. You will be prompted for the key passphrase and Admin PIN.
gpg> key 1
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: C
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb* rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: S
ssb rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: E
ssb rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: A
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
gpg> keytocard
Please select where to store the key:
(1) Signature key
(3) Authentication key
Your selection? 1
You need a passphrase to unlock the secret key for
user: "Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>"
4096-bit RSA key, ID 0xBECFA3C1AE191D15, created 2016-05-24
Encryption
Type key 1 again to de-select and key 2 to select the next key:
gpg> key 1
gpg> key 2
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: C
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: S
ssb* rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: E
ssb rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: A
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
gpg> keytocard
Please select where to store the key:
(2) Encryption key
Your selection? 2
[...]
Authentication
Type key 2 again to deselect and key 3 to select the last key:
gpg> key 2
gpg> key 3
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
created: 2017-10-09 expires: never usage: C
trust: ultimate validity: ultimate
ssb rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: S
ssb rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: E
ssb* rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D
created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: A
[ultimate] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
gpg> keytocard
Please select where to store the key:
(3) Authentication key
Your selection? 3
gpg> save
Verify card
Verify the sub-keys have been moved to YubiKey as indicated by ssb>:
$ gpg -K
/tmp.FLZC0xcM/pubring.kbx
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
sec rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB 2017-10-09 [C]
Key fingerprint = 011C E16B D45B 27A5 5BA8 776D FF3E 7D88 647E BCDB
uid Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
ssb> rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15 2017-10-09 [S] [expires: 2018-10-09]
ssb> rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF 2017-10-09 [E] [expires: 2018-10-09]
ssb> rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D 2017-10-09 [A] [expires: 2018-10-09]
Cleanup
Ensure you have:
- Saved the encryption, signing and authentication sub-keys to YubiKey.
- Saved the YubiKey PINs which you changed from defaults.
- Saved the password to the master key.
- Saved a copy of the master key, sub-keys and revocation certificates on an encrypted volume, to be stored offline.
- Saved the password to that encrypted volume in a separate location.
- Saved a copy of the public key somewhere easily accessible later.
Reboot or securely delete $GNUPGHOME and remove the secret keys from the GPG keyring:
$ sudo srm -r $GNUPGHOME || sudo rm -rf $GNUPGHOME
$ gpg --delete-secret-key $KEYID
Important Make sure you have securely erased all generated keys and revocation certificates if an ephemeral enviroment was not used!
Using keys
Download drduh/config/gpg.conf:
$ cd ~/.gnupg ; wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/drduh/config/master/gpg.conf
$ chmod 600 gpg.conf
Install the required packages and mount the non-encrypted volume created earlier:
Linux
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y \
gnupg2 gnupg-agent gnupg-curl scdaemon pcscd
$ sudo mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt
OpenBSD
$ doas pkg_add gnupg pcsc-tools
$ doas mount /dev/sd2b /mnt
Import the public key:
$ gpg --import /mnt/pubkey.txt
gpg: key 0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB: public key "Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>" imported
gpg: Total number processed: 1
gpg: imported: 1
Or download the public key from a keyserver:
$ gpg --recv $KEYID
gpg: requesting key 0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB from hkps server hkps.pool.sks-keyservers.net
[...]
gpg: key 0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB: public key "Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>" imported
gpg: Total number processed: 1
gpg: imported: 1
Edit the master key to assign it ultimate trust by selecting trust and 5:
$ export KEYID=0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
$ gpg --edit-key $KEYID
gpg> trust
pub 4096R/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB created: 2016-05-24 expires: never usage: C
trust: unknown validity: unknown
sub 4096R/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15 created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: S
sub 4096R/0x5912A795E90DD2CF created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: E
sub 4096R/0x3F29127E79649A3D created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: A
[ unknown] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
Please decide how far you trust this user to correctly verify other users' keys
(by looking at passports, checking fingerprints from different sources, etc.)
1 = I don't know or won't say
2 = I do NOT trust
3 = I trust marginally
4 = I trust fully
5 = I trust ultimately
m = back to the main menu
Your decision? 5
Do you really want to set this key to ultimate trust? (y/N) y
pub 4096R/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB created: 2016-05-24 expires: never usage: C
trust: ultimate validity: unknown
sub 4096R/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15 created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: S
sub 4096R/0x5912A795E90DD2CF created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: E
sub 4096R/0x3F29127E79649A3D created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09 usage: A
[ unknown] (1). Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
gpg> quit
Remove and re-insert YubiKey and check the status:
$ gpg --card-status
Application ID ...: D2760001240102010006055532110000
Version ..........: 2.1
Manufacturer .....: Yubico
Serial number ....: 05553211
Name of cardholder: Dr Duh
Language prefs ...: en
Sex ..............: unspecified
URL of public key : [not set]
Login data .......: doc@duh.to
Signature PIN ....: not forced
Key attributes ...: 4096R 4096R 4096R
Max. PIN lengths .: 127 127 127
PIN retry counter : 3 3 3
Signature counter : 0
Signature key ....: 07AA 7735 E502 C5EB E09E B8B0 BECF A3C1 AE19 1D15
created ....: 2016-05-24 23:22:01
Encryption key....: 6F26 6F46 845B BEB8 BDF3 7E9B 5912 A795 E90D D2CF
created ....: 2016-05-24 23:29:03
Authentication key: 82BE 7837 6A3F 2E7B E556 5E35 3F29 127E 7964 9A3D
created ....: 2016-05-24 23:36:40
General key info..: pub 4096R/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15 2016-05-24 Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
sec# 4096R/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB created: 2016-05-24 expires: never
ssb> 4096R/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15 created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09
card-no: 0006 05553211
ssb> 4096R/0x5912A795E90DD2CF created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09
card-no: 0006 05553211
ssb> 4096R/0x3F29127E79649A3D created: 2017-10-09 expires: 2018-10-09
card-no: 0006 05553211
sec# indicates master key is not available (as it should be stored encrypted offline).
Note If you see General key info..: [none] in the output instead - go back and import the public key using the previous step.
Encrypt a message to your own key (useful for storing password credentials and other data):
$ echo "test message string" | gpg --encrypt --armor --recipient $KEYID -o encrypted.txt
To encrypt to multiple recipients (or to multiple keys):
$ echo "test message string" | gpg --encrypt --armor --recipient $KEYID_0 --recipient $KEYID_1 --recipient $KEYID_2 -o encrypted.txt
Decrypt the message:
$ gpg --decrypt --armor encrypted.txt
gpg: anonymous recipient; trying secret key 0x0000000000000000 ...
gpg: okay, we are the anonymous recipient.
gpg: encrypted with RSA key, ID 0x0000000000000000
test message string
Sign a message:
$ echo "test message string" | gpg --armor --clearsign > signed.txt
Verify the signature:
$ gpg --verify signed.txt
gpg: Signature made Wed 25 May 2016 00:00:00 AM UTC
gpg: using RSA key 0xBECFA3C1AE191D15
gpg: Good signature from "Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>" [ultimate]
Primary key fingerprint: 011C E16B D45B 27A5 5BA8 776D FF3E 7D88 647E BCDB
Subkey fingerprint: 07AA 7735 E502 C5EB E09E B8B0 BECF A3C1 AE19 1D15
Rotating keys
PGP does not provide forward secrecy - a compromised key may be used to decrypt all past messages. Although keys stored on YubiKey are difficult to steal, it is not impossible - the key and PIN could be taken, or a vulnerability may be discovered in key hardware or random number generator used to create them, for example. Therefore, it is good practice to occassionally rotate sub-keys.
When a sub-key expires, it can either be renewed or replaced. Both actions require access to the offline master key. Renewing sub-keys by updating their expiration date indicates you are still in possession of the offline master key and is more convenient.
Replacing keys, on the other hand, is less convenient but more secure: the new sub-keys will not be able to decrypt previous messages, authenticate with SSH, etc. Contacts will need to receive the updated public key and any encrypted secrets need to be decrypted and re-encrypted to new sub-keys to be usable. This process is functionally equivalent to "losing" the YubiKey and provisioning a new one. However, you will always be able to decrypt previous messages using the offline encrypted backup of the original keys.
Neither rotation method is superior and it's up to personal philosophy on identity management and individual threat model to decide which one to use, or whether to expire sub-keys at all. Ideally, sub-keys would be ephemeral: used only once for each encryption, signing and authentication event, however in practice that is not really feasible or worthwhile with YubiKey. Advanced users may want to dedicate an offline device for more frequent key rotations and ease of provisioning.
To renew or rotate sub-keys, follow the same procedure to boot to a secure environment. Install required software and disconnect networking. Decrypt and mount the offline volume, then import the master key and configuration to a temporary working directory:
$ export GNUPGHOME=$(mktemp -d)
$ gpg --import /mnt/encrypted-usb/tmp.XXX/mastersub.key
$ cp -v /mnt/encrypted-usb/tmp.XXX/gpg.conf $GNUPGHOME
Edit the master key:
$ export KEYID=0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB
$ gpg --edit-key $KEYID
Secret key is available
[...]
Follow the original steps to generate each sub-key. Previous sub-keys may be kept or deleted from the identity.
Finish by exporting new keys:
$ gpg --armor --export-secret-keys $KEYID > $GNUPGHOME/mastersub.key
$ gpg --armor --export-secret-subkeys $KEYID > $GNUPGHOME/sub.key
Copy the new temporary working directory to encrypted offline storage, which should still be mounted:
$ sudo cp -avi $GNUPGHOME /mnt/encrypted-usb
There should now be at least two versions of the master and sub-keys backed up:
$ ls /mnt/encrypted-usb
lost+found tmp.ykhTOGjR36 tmp.2gyGnyCiHs
Unmount and close the encrypted volume:
$ sudo umount /mnt/encrypted-usb
$ sudo cryptsetup luksClose /dev/mapper/usb/
Export the updated public key:
$ sudo mkdir /mnt/public
$ sudo mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt/public
$ gpg --armor --export $KEYID | sudo tee /mnt/public/$KEYID-$(date +%F).txt
$ sudo umount /mnt/public
Disconnect the storage device and follow the original steps to transfer new keys (4, 5 and 6) to YubiKey, replacing existing ones. Reboot or securely erase the GPG temporary working directory.
SSH
gpg-agent supports the OpenSSH ssh-agent protocol (enable-ssh-support), as well as Putty's Pageant on Windows (enable-putty-support). This means it can be used instead of the traditional ssh-agent / pageant. There are some differences from ssh-agent, notably that gpg-agent does not cache keys rather it converts, encrypts and stores them - persistently - as GPG keys and then makes them available to ssh clients. Any existing ssh private keys that you'd like to keep in gpg-agent should be deleted after they've been imported to the GPG agent.
When importing the key to gpg-agent, you'll be prompted for a passphrase to protect that key within GPG's key store - you may want to use the same passphrase as the original's ssh version. GPG can both cache passphrases for a determined period (ref. gpg-agent's various cache-ttl options), and since version 2.1 can store and fetch passphrases via the macOS keychain. Note than when removing the old private key after importing to gpg-agent, keep the .pub key file around for use in specifying ssh identities (e.g. ssh -i /path/to/identity.pub).
Probably the biggest thing missing from gpg-agent's ssh agent support is being able to remove keys. ssh-add -d/-D have no effect. Instead, you need to use the gpg-connect-agent utility to lookup a key's keygrip, match that with the desired ssh key fingerprint (as an MD5) and then delete that keygrip. The gnupg-users mailing list has more information.
Create configuration
Create a hardened configuration for gpg-agent by downloading drduh/config/gpg-agent.conf:
$ cd ~/.gnupg
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/drduh/config/master/gpg-agent.conf
$ grep -ve "^#" gpg-agent.conf
enable-ssh-support
default-cache-ttl 60
max-cache-ttl 120
pinentry-program /usr/bin/pinentry-curses
Tip Set pinentry-program /usr/bin/pinentry-gnome3 for a GUI-based prompt.
On macOS, use brew install pinentry-mac and adjust the program path to suit.
Replace agents
To launch gpg-agent for use by SSH, use the gpg-connect-agent /bye or gpgconf --launch gpg-agent commands.
Add these to the shell rc file:
export GPG_TTY="$(tty)"
export SSH_AUTH_SOCK="/run/user/$UID/gnupg/S.gpg-agent.ssh"
gpg-connect-agent updatestartuptty /bye > /dev/null
On modern systems, you can use the following instead, as gpgconf --list-dirs agent-ssh-socket will automatically set SSH_AUTH_SOCK to the correct value; and is therefore typically better than hard-coding to run/user/$UID/gnupg/S.gpg-agent.ssh, if available:
export GPG_TTY="$(tty)"
export SSH_AUTH_SOCK=$(gpgconf --list-dirs agent-ssh-socket)
gpgconf --launch gpg-agent
Note that SSH_AUTH_SOCK normally only needs to be set on the local laptop (workstation), where the YubiKey is plugged in. On the remote server that we SSH into, ssh will automatically set SSH_AUTH_SOCK to something like /tmp/ssh-mXzCzYT2Np/agent.7541 when we connect. We therefore do NOT manually set SSH_AUTH_SOCK on the server. (Doing so would break SSH Agent Forwarding.)
Copy public key
Note It is not necessary to import the corresponding GPG public key in order to use SSH.
Copy and paste the output from ssh-add to the server's authorized_keys file:
$ ssh-add -L
ssh-rsa AAAAB4NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAz[...]zreOKM+HwpkHzcy9DQcVG2Nw== cardno:000605553211
(Optional) Save public key for identity file configuration
By default, SSH attempts to use all the identities available via the agent. It's often a good idea to manage exactly which keys SSH will use to connect to a server, for example to separate different roles or to avoid being fingerprinted by untrusted ssh servers. To do this you'll need to use the command line argument -i [identity_file] or the IdentityFile and IdentitiesOnly options in .ssh/config.
The argument provided to IdentityFile is traditionally the path to the private key file (for example IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa). For the YubiKey - indeed, in general for keys stored in an ssh agent - IdentityFile should point to the public key file, ssh will select the appropriate private key from those available via the ssh agent. To prevent ssh from trying all keys in the agent use the IdentitiesOnly yes option along with one or more -i or IdentityFile options for the target host.
To reiterate, with IdentitiesOnly yes, ssh will not automatically enumerate public keys loaded into ssh-agent or gpg-agent. This means publickey authentication will not proceed unless explicitly named by ssh -i [identity_file] or in .ssh/config on a per-host basis.
In the case of YubiKey usage, to extract the public key from the ssh agent:
$ ssh-add -L | grep "cardno:000605553211" > ~/.ssh/id_rsa_yubikey.pub
Then you can explicitly associate this YubiKey-stored key for used with a host, github.com for example, as follows:
$ cat << EOF >> ~/.ssh/config
Host github.com
IdentitiesOnly yes
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_yubikey.pub
EOF
Connect with public key authentication
$ ssh git@github.com -vvv
[...]
debug2: key: cardno:000605553211 (0x1234567890),
debug1: Authentications that can continue: publickey
debug3: start over, passed a different list publickey
debug3: preferred gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic,publickey,keyboard-interactive,password
debug3: authmethod_lookup publickey
debug3: remaining preferred: keyboard-interactive,password
debug3: authmethod_is_enabled publickey
debug1: Next authentication method: publickey
debug1: Offering RSA public key: cardno:000605553211
debug3: send_pubkey_test
debug2: we sent a publickey packet, wait for reply
debug1: Server accepts key: pkalg ssh-rsa blen 535
debug2: input_userauth_pk_ok: fp e5:de:a5:74:b1:3e:96:9b:85:46:e7:28:53:b4:82:c3
debug3: sign_and_send_pubkey: RSA e5:de:a5:74:b1:3e:96:9b:85:46:e7:28:53:b4:82:c3
debug1: Authentication succeeded (publickey).
[...]
Note To make multiple connections or securely transfer many files, consider using the ControlMaster ssh option. Also see drduh/config/ssh_config.
Import SSH keys
If there are existing SSH keys that you wish to make available via gpg-agent, you'll need to import them. You should then remove the original private keys. When importing the key, gpg-agent uses the key's filename as the key's label; this makes it easier to follow where the key originated from. In this example, we're starting with just the YubiKey's key in place and importing ~/.ssh/id_rsa:
$ ssh-add -l
4096 SHA256:... cardno:00060123456 (RSA)
$ ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa && rm ~/.ssh/id_rsa
When invoking ssh-add, it will prompt for the SSH key's passphrase if present, then the pinentry program will prompt and confirm for a new passphrase to use to encrypt the converted key within the GPG key store.
The migrated key should be listed in ssh-add -l:
$ ssh-add -l
4096 SHA256:... cardno:00060123456 (RSA)
2048 SHA256:... /Users/username/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA)
Or to show the keys with MD5 fingerprints, as used by gpg-connect-agent's KEYINFO and DELETE_KEY commands:
$ ssh-add -E md5 -l
4096 MD5:... cardno:00060123456 (RSA)
2048 MD5:... /Users/username/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA)
When using the key pinentry will be invoked to request the key's passphrase. The passphrase will be cached for up to 10 minutes idle time between uses, to a maximum of 2 hours.
Remote Machines (Agent Forwarding)
Note SSH Agent Forwarding can add additional risk - proceed with caution!
To use YubiKey to sign a git commit on a remote host, or ssh through another network, configure and use Agent Forwarding.
To do this, you need access to the remote machine and the YubiKey has to be set up on the host machine.
On the remote machine, edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config to set StreamLocalBindUnlink yes
Optional If you do not have root access to the remote machine to edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config, you will need to remove the socket on the remote machine before forwarding works. For example, rm /run/user/1000/gnupg/S.gpg-agent. Further information can be found on the AgentForwarding GNUPG wiki page.
Import public keys to the remote machine. This can be done by fetching from a keyserver. On the local machine, copy the public keyring to the remote machine:
$ scp ~/.gnupg/pubring.kbx remote:~/.gnupg/
You should now be able use ssh -A remote on the local machine to log into remote, and should then be able to use YubiKey as if it were connected to the remote machine. For example, using e.g. ssh-add -l on that remote machine should show the public key from the YubiKey (note cardno:). (If you don't want to have to remember to use ssh -A, you can use ForwardAgent yes in ~/.ssh/config. As a security best practice, always use ForwardAgent yes only for a single Hostname, never for all servers.)
On modern distributions, such as Fedora 30, there is typically no need to also set RemoteForward in ~/.ssh/config as detailed in the next chapter, because the right thing actually happens automatically.
Steps for older distributions
On the local machine, run:
$ gpgconf --list-dirs agent-extra-socket
This should return a path to agent-extra-socket - /run/user/1000/gnupg/S.gpg-agent.extra - though on older Linux distros (and macOS) it may be /home/<user>/.gnupg/S/gpg-agent.extra
Find the agent socket on the remote machine:
$ gpgconf --list-dirs agent-socket
This should return a path such as /run/user/1000/gnupg/S.gpg-agent
Finally, enable agent forwarding for a given machine by adding the following to the local machine's ssh config file ~/.ssh/config (your agent sockets may be different):
Host
Hostname remote-host.tld
ForwardAgent yes
RemoteForward /run/user/1000/gnupg/S.gpg-agent /run/user/1000/gnupg/S.gpg-agent.extra
# RemoteForward [remote socket] [local socket]
If you're still having problems, it may be necessary to edit gpg-agent.conf file on both the remote and local machines to add the following information:
enable-ssh-support
pinentry-program /usr/bin/pinentry-curses
extra-socket /run/user/1000/gnupg/S.gpg-agent.extra
See Issue #85 for more information and troubleshooting.
GitHub
You can use YubiKey to sign GitHub commits and tags. It can also be used for GitHub SSH authentication, allowing you to push, pull, and commit without a password.
Login to GitHub and upload SSH and PGP public keys in Settings.
To configure a signing key:
> git config --global user.signingkey $KEYID
Make sure the user.email option matches the email address associated with the PGP identity.
Now, to sign commits or tags simply use the -S option. GPG will automatically query YubiKey and prompt you for a PIN.
To authenticate:
Windows
Run the following command:
> git config --global core.sshcommand 'plink -agent'
You can then change the repository url to git@github.com:USERNAME/repository and any authenticated commands will be authorized by YubiKey.
Note If you encounter the error gpg: signing failed: No secret key - run gpg --card-status with YubiKey plugged in and try the git command again.
OpenBSD
Install and enable tools for use with PC/SC drivers, cards, readers, then reboot to recognize YubiKey:
$ doas pkg_add pcsc-tools
$ doas rcctl enable pcscd
$ doas reboot
Windows
Windows can already have some virtual smartcard readers installed, like the one provided for Windows Hello. To ensure your YubiKey is the correct one used by scdaemon, you should add it to its configuration. You will need your device's full name. To find out what is your device's full name, plug your YubiKey, open the Device Manager, select "View->Show hidden devices". Go to the Software Devices list, you should see something like Yubico YubiKey OTP+FIDO+CCID 0. The name slightly differs according to the model. Thanks to Scott Hanselman for sharing this information.
- Create or edit %APPDATA%/gnupg/scdaemon.conf, add
reader-port <your yubikey device's full name>. - In %APPDATA%/gnupg/gpg-agent.conf, add:
enable-ssh-support
enable-putty-support
- Open a command console, restart the agent:
> gpg-connect-agent killagent /bye
> gpg-connect-agent /bye
- Enter
> gpg --card-statusto see YubiKey details. - Import the public key:
> gpg --import <path to public key file> - Trust it: Trust master key
- Retrieve the public key id:
> gpg --list-public-keys - Export the SSH key from GPG:
> gpg --export-ssh-key <public key id>
Copy this key to a file for later use. It represents the public SSH key corresponding to the secret key on the YubiKey. You can upload this key to any server you wish to SSH into.
- Create a shortcut that points to
gpg-connect-agent /byeand place it in the startup foldershell:startupto make sure the agent starts after a system shutdown. Modify the shortcut properties so it starts in a "Minimized" window, to avoid unnecessary noise at startup.
Now you can use PuTTY for public key SSH authentication. When the server asks for public key verification, PuTTY will forward the request to GPG, which will prompt you for a PIN and authorize the login using YubiKey.
WSL
The goal here is to make the SSH client inside WSL work together with the Windows agent you are using (gpg-agent.exe in our case). Here is what we are going to achieve:
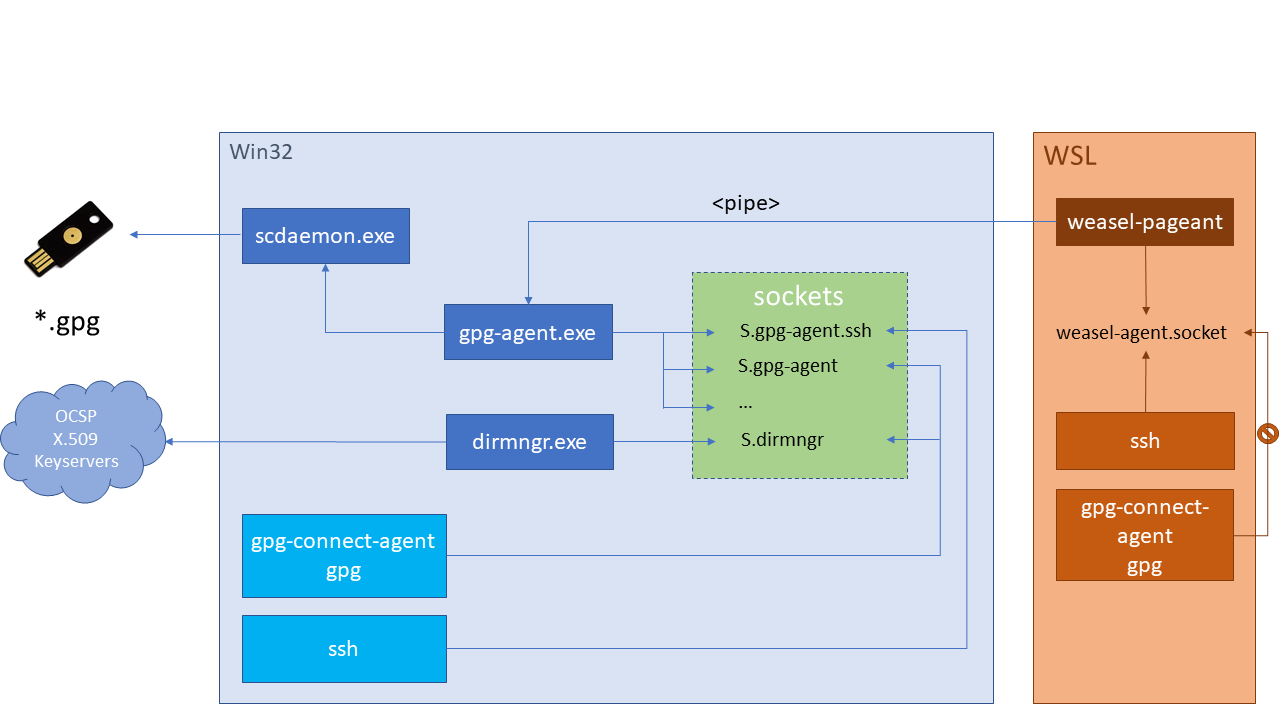
Note this works only for SSH agent forwarding. Real GPG forwarding (encryption/decryption) is actually not supported. See the weasel-pageant readme for further information.
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu 16.04 or newer for WSL
- Kleopatra
- Windows configuration
WSL configuration
Download or clone weasel-pageant.
Add eval $(/mnt/c/<path of extraction>/weasel-pageant -r -a /tmp/S.weasel-pageant) to shell rc file. Use a named socket here so it can be used in the RemoteForward directive of ~/.ssh/config. Source it with source ~/.bashrc.
Display the SSH key with $ ssh-add -l
Edit ~/.ssh/config to add the following for each host you want to use agent forwarding:
ForwardAgent yes
RemoteForward <remote ssh socket path> /tmp/S.weasel-pageant
Note The remote ssh socket path can be found with gpgconf --list-dirs agent-ssh-socket
Remote host configuration
You may have to add the following to the shell rc file: (On Linux, this is only required on the laptop/workstation where the YubiKey is plugged in, and NOT on the remote host server that you connect to; in fact at least on some Linux distributions, changing SSH_AUTH_SOCK on the server breaks agent forwarding.)
export SSH_AUTH_SOCK=$(gpgconf --list-dirs agent-ssh-socket)
export GPG_TTY=$(tty)
Add the following to /etc/ssh/sshd_config:
AllowAgentForwarding yes
StreamLocalBindUnlink yes
And reload the SSH daemon (e.g., sudo service sshd reload).
Unplug YubiKey, disconnect or reboot. Log back in to Windows, open a WSL console and enter ssh-add -l - you should see nothing.
Plug in YubiKey, enter the same command to display the ssh key.
Log in to the remote host, you should have the pinentry dialog asking for the YubiKey pin.
On the remote host, type ssh-add -l - if you see the ssh key, that means forwarding works!
Note Agent forwarding may be chained through multiple hosts - just follow the same protocol to configure each host.
Multiple Keys
To use a single identity with multiple YubiKeys - or to replace a lost card with another - issue this command to switch keys:
$ gpg-connect-agent "scd serialno" "learn --force" /bye
Alternatively, you could manually delete the GnuPG shadowed key - where the card serial number is stored (see GnuPG #T2291).
Find the Keygrip number of each key:
$ gpg --with-keygrip -k $KEYID
pub rsa4096/0xFF3E7D88647EBCDB 2017-10-09 [C]
Key fingerprint = 011C E16B D45B 27A5 5BA8 776D FF3E 7D88 647E BCDB
Keygrip = 7A20855980A62C10569DE893157F38A696B1300E
uid [ ultime ] Dr Duh <doc@duh.to>
sub rsa4096/0xBECFA3C1AE191D15 2017-10-09 [S] [expires: 2018-10-09]
Keygrip = 85D44BD52AD45C0852BD15BF41161EE9AE477398
sub rsa4096/0x5912A795E90DD2CF 2017-10-09 [E] [expires: 2018-10-09]
Keygrip = A0AA3D9F626BDEA3B833F290C7BCA79216C8A996
sub rsa4096/0x3F29127E79649A3D 2017-10-09 [A] [expires: 2018-10-09]
Keygrip = 7EF25A1115294342F451BC1CDD0FA94395F2D074
Delete all the shadow keys using their Keygrip number:
$ cd ~/.gnupg/private-keys-v1.d
$ rm 85D44BD52AD45C0852BD15BF41161EE9AE477398.key \
A0AA3D9F626BDEA3B833F290C7BCA79216C8A996.key \
7EF25A1115294342F451BC1CDD0FA94395F2D074.key
Insert the new YubiKey and re-generate shadow-keys by checking card status:
$ gpg --card-status
See discussion in Issues #19 and #112 for more information and troubleshooting steps.
Require touch
Note This is not possible on YubiKey NEO.
By default, YubiKey will perform encryption, signing and authentication operations without requiring any action from the user, after the key is plugged in and first unlocked with the PIN.
To require a touch for each key operation, install YubiKey Manager and recall the Admin PIN:
Note Older versions of the YubiKey Manager used touch instead of set-touch in the below commands.
Authentication:
$ ykman openpgp set-touch aut on
Signing:
$ ykman openpgp set-touch sig on
Encryption:
$ ykman openpgp set-touch enc on
YubiKey will blink when it is waiting for a touch.
GPG keys on YubiKey can be used with ease to encrypt and/or sign emails and attachments using Thunderbird and Enigmail. Thunderbird supports OAuth 2 authentication and can be used with Gmail. See this guide from EFF for detailed instructions.
mailvelope on MacOS
Mailvelope allows GPG keys on YubiKey to be used with Gmail and others.
On MacOS install gpgme using homebrew:
$ brew install gpgme
To allow Chrome to run gpgme:
$ nano ~/Library/Application\ Support/Google/Chrome/NativeMessagingHosts/gpgmejson.json
and paste:
{
"name": "gpgmejson",
"description": "Integration with GnuPG",
"path": "/usr/local/bin/gpgme-json",
"type": "stdio",
"allowed_origins": [
"chrome-extension://kajibbejlbohfaggdiogboambcijhkke/"
]
}
Edit the default path to allow Chrome to find gpg:
$ sudo launchctl config user path /usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin
Close Chrome if it is running and reboot your Mac.
Finally install the mailvelope extension from the Chrome app store.
Reset
If PIN attempts are exceeded, the card is locked and must be reset and set up again using the encrypted backup.
Copy the following script to a file and run gpg-connect-agent -R $file to lock and terminate the card. Then re-insert YubiKey to reset.
/hex
scd serialno
scd apdu 00 20 00 81 08 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 40
scd apdu 00 20 00 81 08 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 40
scd apdu 00 20 00 81 08 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 40
scd apdu 00 20 00 81 08 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 40
scd apdu 00 20 00 83 08 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 40
scd apdu 00 20 00 83 08 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 40
scd apdu 00 20 00 83 08 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 40
scd apdu 00 20 00 83 08 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 40
scd apdu 00 e6 00 00
scd apdu 00 44 00 00
/echo Card has been successfully reset.
Notes
- YubiKey has two configurations: one invoked with a short press, and the other with a long press. By default, the short-press mode is configured for HID OTP - a brief touch will emit an OTP string starting with
cccccccc. If you rarely use the OTP mode, you can swap it to the second configuration via the YubiKey Personalization tool. If you never use OTP, you can disable it entirely using the YubiKey Manager application (note, this not the similarly named older YubiKey NEO Manager). - Programming YubiKey for GPG keys still lets you use its other configurations - U2F, OTP and static password modes, for example.
- Setting an expiry essentially forces you to manage your subkeys and announces to the rest of the world that you are doing so. Setting an expiry on a primary key is ineffective for protecting the key from loss - whoever has the primary key can simply extend its expiry period. Revocation certificates are better suited for this purpose. It may be appropriate for your use case to set expiry dates on subkeys.
- To switch between two or more identities on different keys - unplug the first key and restart gpg-agent, ssh-agent and pinentry with
pkill gpg-agent ; pkill ssh-agent ; pkill pinentry ; eval $(gpg-agent --daemon --enable-ssh-support), then plug in the other key and rungpg-connect-agent updatestartuptty /bye- then it should be ready for use.
Troubleshooting
-
Use
man gpgto understand GPG options and command-line flags. -
If you encounter problems connecting to YubiKey with GPG - try unplugging and re-inserting YubiKey, and restarting the
gpg-agentprocess. -
If you receive the error,
gpg: decryption failed: secret key not available- you likely need to install GnuPG version 2.x. -
If you receive the error,
Yubikey core error: no yubikey present- make sure the YubiKey is inserted correctly. It should blink once when plugged in. -
If you still receive the error,
Yubikey core error: no yubikey present- you likely need to install newer versions of yubikey-personalize as outlined in Required software. -
If you receive the error,
Yubikey core error: write error- YubiKey is likely locked. Install and run yubikey-personalization-gui to unlock it. -
If you receive the error,
Key does not match the card's capability- you likely need to use 2048 bit RSA key sizes. -
If you receive the error,
sign_and_send_pubkey: signing failed: agent refused operation- make sure you replacedssh-agentwithgpg-agentas noted above. -
If you still receive the error,
sign_and_send_pubkey: signing failed: agent refused operation- run the commandgpg-connect-agent updatestartuptty /bye -
If you still receive the error,
sign_and_send_pubkey: signing failed: agent refused operation- check~/.gnupg/gpg-agent.confto make sure the path topinentryis correct. -
If you receive the error,
Error connecting to agent: No such file or directoryfromssh-add -L, the UNIX file socket that the agent uses for communication with other processes may not be set up correctly. On Debian, tryexport SSH_AUTH_SOCK="/run/user/$UID/gnupg/S.gpg-agent.ssh". Also see thatgpgconf --list-dirs agent-ssh-socketis returning single path, to existingS.gpg-agent.sshsocket. -
If you receive the error,
Permission denied (publickey), increase ssh verbosity with the-vflag and ensure the public key from the card is being offered:Offering public key: RSA SHA256:abcdefg... cardno:00060123456. If it is, ensure you are connecting as the right user on the target system, rather than as the user on the local system. Otherwise, be sureIdentitiesOnlyis not enabled for this host. -
If SSH authentication still fails - add up to 3
-vflags to thesshclient to increase verbosity. -
If it still fails, it may be useful to stop the background
sshddaemon process service on the server (e.g. usingsudo systemctl stop sshd) and instead start it in the foreground with extensive debugging output, usingsshd -eddd. Note that (quoteman sshd) The server also will not fork and will only process one connection., and therefore has to be re-started after everysshtest.
Links
- https://alexcabal.com/creating-the-perfect-gpg-keypair/
- https://blog.habets.se/2013/02/GPG-and-SSH-with-Yubikey-NEO
- https://blog.josefsson.org/2014/06/23/offline-gnupg-master-key-and-subkeys-on-yubikey-neo-smartcard/
- https://blog.onefellow.com/post/180065697833/yubikey-forwarding-ssh-keys
- https://developers.yubico.com/PGP/Card_edit.html
- https://developers.yubico.com/PIV/Introduction/Admin_access.html
- https://developers.yubico.com/yubico-piv-tool/YubiKey_PIV_introduction.html
- https://developers.yubico.com/yubikey-personalization/
- https://developers.yubico.com/yubikey-piv-manager/PIN_and_Management_Key.html
- https://evilmartians.com/chronicles/stick-with-security-yubikey-ssh-gnupg-macos
- https://gist.github.com/ageis/14adc308087859e199912b4c79c4aaa4
- https://github.com/herlo/ssh-gpg-smartcard-config
- https://github.com/tomlowenthal/documentation/blob/master/gpg/smartcard-keygen.md
- https://help.riseup.net/en/security/message-security/openpgp/best-practices
- https://jclement.ca/articles/2015/gpg-smartcard/
- https://rnorth.org/gpg-and-ssh-with-yubikey-for-mac
- https://trmm.net/Yubikey
- https://www.bootc.net/archives/2013/06/09/my-perfect-gnupg-ssh-agent-setup/
- https://www.esev.com/blog/post/2015-01-pgp-ssh-key-on-yubikey-neo/
- https://www.hanselman.com/blog/HowToSetupSignedGitCommitsWithAYubiKeyNEOAndGPGAndKeybaseOnWindows.aspx
- https://www.void.gr/kargig/blog/2013/12/02/creating-a-new-gpg-key-with-subkeys/
- https://mlohr.com/gpg-agent-forwarding/